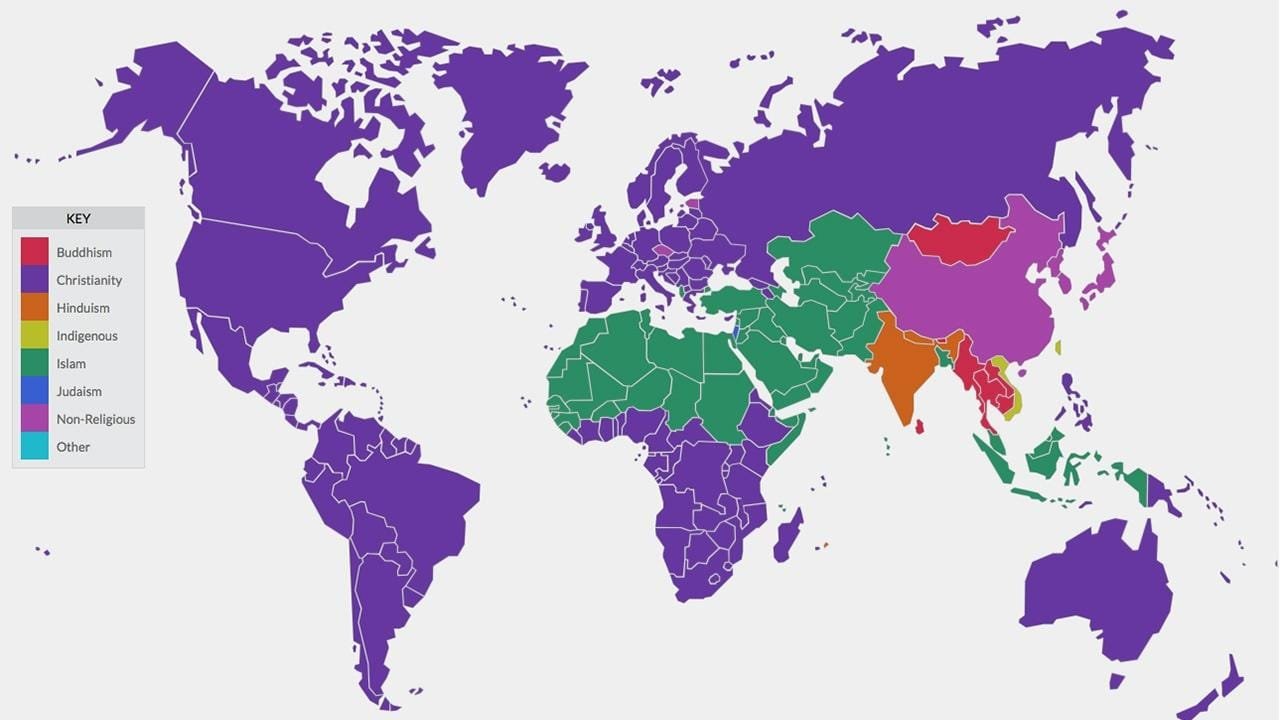
Have you ever wondered how different countries approach religious education? Considering how diverse and multifaceted religious beliefs and teachings are across the globe, it can be fascinating to explore how these are reflected in educational systems. By shedding light on various methods, we can better understand each culture’s relationship with religion, as well as the role education plays in shaping these perceptions.
Understanding Religious Education Globally
Religious education is a formal instruction about specific religious beliefs, practices, and values. Globally, the approach to religious education can vary significantly, often influenced by the country’s history, predominant religions, and socio-political context. While some nations integrate religious studies into public education, others offer it as an elective or delegate such teachings to private institutions or parental discretion. Religious education can serve as an important tool for promoting mutual respect, understanding, and coexistence among diverse communities.
Diverse Approaches Across the World
Religious Education in Secular vs. Religious States
One of the major distinctions in religious education is the difference between secular and religious states. In countries like the United States or France, which uphold a strict separation between state and religion, religious education in public schools tends to focus on comparative religion or secular studies. This means exploring a variety of world religions from a neutral standpoint, fostering an understanding of different faiths without endorsing any one belief system.
Theocratic Influences
In contrast, theocratic nations or those with a state-endorsed religion can exhibit a more singular focus in religious education. For instance, Saudi Arabia, where Islam is the state religion, includes extensive studies of Islamic teachings and principles as part of its curriculum. Such countries often seek to intertwine religious teachings with daily governance and public life.
Cultural Contexts and Religious Studies
Countries with rich cultural tapestries often tailor their religious education to reflect local traditions and values. For example, India has a diverse religious landscape including Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Islam, and Christianity. Consequently, its educational framework allows for religious instruction but typically mandates a more flexible approach that respects this diversity while also emphasizing cultural cohesion.
Understanding Religious Education: Key Questions Answered
How Is Religious Education Structured?
Religious education can be structured in various ways, depending on the context:
- Mandatory Courses: Some countries require students to partake in religious education as part of their basic curriculum.
- Elective Courses: Others offer it as an elective, allowing students and parents to choose based on personal beliefs.
- Private Religious Instruction: In some regions, religious education is primarily offered through religious institutions or community groups outside the public school system.
How Does Religious Education Impact Society?
The impact of religious education can be profound:
- Promotes Tolerance and Understanding: By learning about different religious beliefs, students often develop greater empathy and understanding of diverse worldviews.
- Shapes Cultural Identity: In many places, religious education reinforces cultural norms and helps preserve traditional practices.
- Encourages Moral Development: Religious teachings often focus on moral and ethical guidance, aimed at shaping the values and behaviors of young individuals.
What Are Some Challenges in Religious Education?
- Secularization: In increasingly secular societies, there’s ongoing debate about the role of religious education in public schools.
- Inclusivity: Balancing respect for diverse beliefs while providing comprehensive religious education remains a significant challenge.
- Contentious Topics: Topics like creationism versus evolution can complicate religious education, especially in science classes.
Case Studies: Global Perspectives on Religious Education
A Look at Norway
Norway exemplifies an interesting blend of religious education, offering courses that cover various world religions, ethics, and philosophical traditions. This approach aims to provide a broad understanding of spirituality and morality without favoring any single religion, aligning with the country’s commitment to secular education.
Religious Instruction in Saudi Arabia
In Saudi Arabia, where Islam plays a central role, religious education is deeply integrated into the curriculum. Students begin learning about Islamic teachings early in life, covering a range of topics from Quranic studies to the Hadiths. This reflects the foundational role of Islam in both society and education.
Japan’s Secular Focus
Japan offers another compelling example, with its largely secular approach to education. Religious instruction is not a regular part of the school curriculum; instead, religious traditions and festivals are celebrated and taught within the cultural and historical contexts, rather than as religious doctrines.
Addressing Myths and Misconceptions
Many Believe Religious Education Promotes Intolerance
A common misconception is that religious education inherently promotes intolerance. In reality, when executed properly, it can do the opposite. By understanding various religious perspectives, students are often equipped to engage more respectfully with people from different backgrounds.
The Myth That Secular Education Excludes All Religious Content
Another myth is that secular education systems completely omit religious content. While religious doctrines might not be taught, many secular systems do include studies on religion that focus on culture, history, and philosophy.
Conclusion: Embracing Diversity in Religious Education
Understanding religious education globally is vital for fostering informed, respectful, and cohesive societies. By exploring different educational approaches, individuals and institutions can appreciate the nuanced ways religion can be included in educational discourse. If you’re interested in further exploring this topic or learning how different educational methods can be applied, consider examining additional resources and studies on religious education practices worldwide.
Related Posts: Effective Strategies for Memorizing Bible Verses from the Old Testament, Understanding the Old and New Testament: A Comparative Study